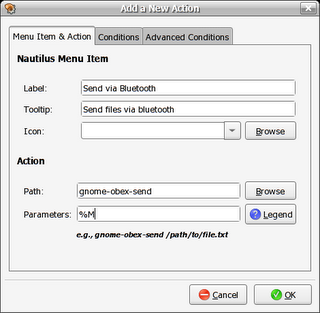
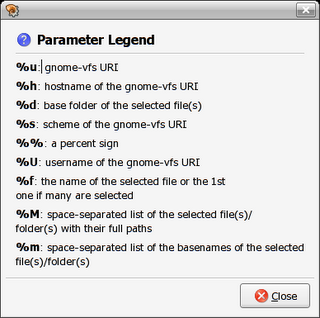
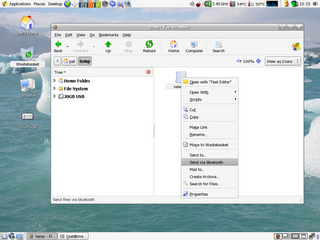
Another new addition to the latest release of Fedora is
avahi support, better known as zeroconf or
bonjour in the Apple world. This allows for service discovery on the network, such as printers automatically anouncing their presence or bookmarks being broadcast to the LAN. The avahi-daemon takes care of advertising services whilst application such as Gnome (2.14) are avahi aware. Here is an example of how to get avahi up and running.
1. Configure some services. The directory /etc/avahi/services is initially empty, so we'll create a few files:
apache.service
ssh-ftp.service
ssh.service
We populate the files with the following data:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone='no'?>
<!DOCTYPE service-group SYSTEM "avahi-service.dtd">
<service-group>
<name>Apache Server Documentation</name>
<service>
<type>_http._tcp</type>
<port>80</port>
<txt-record>path=/manual</txt-record>
</service>
</service-group>
<?xml version="1.0" standalone='no'?>
<!DOCTYPE service-group SYSTEM "avahi-service.dtd">
<service-group>
<name replace-wildcards="yes">SFTP File Transfer on %h</name>
<service>
<type>_sftp-ssh._tcp</type>
<port>22</port>
</service>
</service-group>
<?xml version="1.0" standalone='no'?>
<!DOCTYPE service-group SYSTEM "avahi-service.dtd">
<service-group>
<name replace-wildcards="yes">Remote Terminal on %h</name>
<service>
<type>_ssh._tcp</type>
<port>22</port>
</service>
</service-group>2. Enable the avahi-daemon, and have it auto start on system boot.
# service avahi-daemon start
# chkconfig avahi-daemon on3. We can also enable Gnome file sharing from "Desktop/Preferences/Personal File Sharing" which provides WebDAV access to ~/Public.
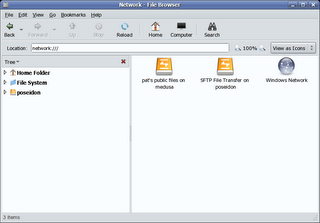
4. If we now start nautilus and click on "network" or go to the "network:///" Gnome-VFS, you can see that in addition to the Windows SMB network we also have the "Public" WebDAV share as well as the secure FTP resources displayed:
5. Epiphany (the Gnome web browser) is the only browser which supports avahi bookmarks at this time. We can see this working if we start Epiphany:
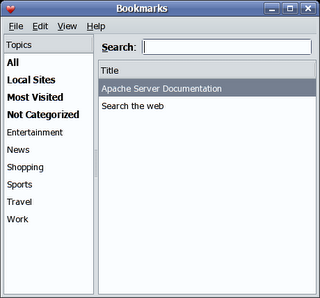
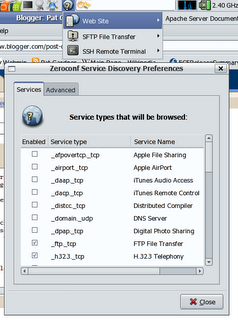
There are a couple of other tools which can display zeroconf services, the avahi provided 'avahi-discover' and the 'Zeroconf discovery applet' which is avaible from the avahi website. Download the service-discovery-applet tarball, unpack and run:
# ./configure && make && make install
You should now be able to add the applet to your gnome-panel:
It's clearly early days for zeroconf support in Linux, but what there is works well. I hope that the Gnome team and other application developers continue to integrate and extend avahi support.