My D-Link print server having been killed by a power surge I needed an alternative method for sharing my printer on the network.
Simple, I thought. Plug it into the USB port of my CentOS server, enable CUPS and away you go. After all, OS X has CUPS built in, doesn't it?
Well..yes, sort of. But as I found out, only Bonjour support is enabled so Lion just doesn't see CUPS broadcasts on the network.
To enable CUPS browsing as well as Bonjour open a terminal and run:
cupsctl BrowseProtocols='"cups dnssd"'
Sunday, July 08, 2012
Thursday, March 15, 2012
GRUB2
I've been trying to get to grips with GRUB2 which has now become the default boot loader on Fedora. In the past if you had wanted to edit the boot menu it was a simple matter of vi'ing /boot/grub/grub.conf
No more.
The new grub configuration file (/boot/grub2/grub.cfg) explicitly states not to edit it manually.
The method now is to edit /etc/default/grub then run this command as root (or sudo):
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
No more.
The new grub configuration file (/boot/grub2/grub.cfg) explicitly states not to edit it manually.
The method now is to edit /etc/default/grub then run this command as root (or sudo):
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
Fedora Desktop Apps
Just finally got around to upgrading my ancient (in Fedora terms) desktop to the shiny new F16. I happen to like Gnome 3; very clean looking.
Anway, a couple of good desktop applications I've discovered that I hadn't been aware until recently are: Hotot (a twitter client) and Vagalume (a last.fm client).
Anway, a couple of good desktop applications I've discovered that I hadn't been aware until recently are: Hotot (a twitter client) and Vagalume (a last.fm client).
Wednesday, July 16, 2008
Solaris 10 ipfilter
Quick guide for ipfilter on Solaris 10
IP Filter home page:
http://coombs.anu.edu.au/~avalon/
Documentation for IPF is also available from:
http://www.freebsd.org/doc/en_US.ISO8859-1/books/handbook/firewalls-ipf.html
Enable interfaces to be used with packet filtering:
Edit /etc/pfil/pfil.ap (old way...now seems to require editing /etc/iu.ap)
Uncomment the device names to enable or add a line to specify the interface:
hme0 -1 0 pfil
For the changes to take effect:
1. svcadm restart /network/pfil and replumb the interfaces
or
2. Reboot
Set the ipfilter service to enabled:
svcadm enable network/ipfilter and replumb the interfaces or reboot
By default the configuration files in /etc/ipf will be read at startup
ipf.conf - ipv4 filtering rules
ipf6.conf - ipv6 filtering rules (if ipv6 is configured)
ipnat.conf - NAT rules (optional)
ippool.conf - refer to many address by a single group name (optional)
A simple ipf.conf to block and log all traffic other than ssh would contain:
pass out quick all keep state
pass in quick on hme0 proto tcp from any to any port = 22 keep state
block in log all
Filtering rules can be loaded from alternative locations:
ipf -f filename
As can NAT rules:
ipnat -f filename
Filter rules sets can either be active or inactive. Doesn't seem to support adding or removing individual rules so the only way of changing the current set seems to be to load an inactive set and to swap that with the running set.
To switch between the active and inactive rule sets:
ipf -s
To modify packet filtering behaviour:
ipf -Fa (remove both incoming and outgoing rule sets)
ipf -Fo (remove outgoing rules only)
ipf -Fi (remove incoming rules only)
ipf -D (disable all packet filtering)
ipf -E (enable packet filtering)
To view currently loaded rules for the active set:
ipfstat -io
To view currently loaded rules for the inactive set:
ipfstat -I -io
To remove all the runnings rules and load a new set from a file:
ipf -Fa -f filename
To load rules to the inactive rule set:
ifp -I -f filename
To append rules to the current active rule set:
echo "block in log on hme0 proto tcp from any to any port = 25" | ipf -f -
Sample rule set for an Solaris 10 host (192.168.93.128) with one zone (192.168.93.132). The interface name is hme0. We all ssh and icmp echo (ping) only to the host, all else being blocked. All outgoing traffic is allowed and stateful. http is allowed through to the Solaris zone hosted on the server:
pass out quick all keep state
pass in quick on hme0 proto icmp from any to any icmp-type 8 keep state
pass in quick on hme0 proto tcp from any to 192.168.93.128 port = ssh keep state
pass in quick on hme0 proto udp from any to 192.168.93.132/32 port = 80 keep state
block in log all
IP Filter home page:
http://coombs.anu.edu.au/~avalon/
Documentation for IPF is also available from:
http://www.freebsd.org/doc/en_US.ISO8859-1/books/handbook/firewalls-ipf.html
Enable interfaces to be used with packet filtering:
Edit /etc/pfil/pfil.ap (old way...now seems to require editing /etc/iu.ap)
Uncomment the device names to enable or add a line to specify the interface:
hme0 -1 0 pfil
For the changes to take effect:
1. svcadm restart /network/pfil and replumb the interfaces
or
2. Reboot
Set the ipfilter service to enabled:
svcadm enable network/ipfilter and replumb the interfaces or reboot
By default the configuration files in /etc/ipf will be read at startup
ipf.conf - ipv4 filtering rules
ipf6.conf - ipv6 filtering rules (if ipv6 is configured)
ipnat.conf - NAT rules (optional)
ippool.conf - refer to many address by a single group name (optional)
A simple ipf.conf to block and log all traffic other than ssh would contain:
pass out quick all keep state
pass in quick on hme0 proto tcp from any to any port = 22 keep state
block in log all
Filtering rules can be loaded from alternative locations:
ipf -f filename
As can NAT rules:
ipnat -f filename
Filter rules sets can either be active or inactive. Doesn't seem to support adding or removing individual rules so the only way of changing the current set seems to be to load an inactive set and to swap that with the running set.
To switch between the active and inactive rule sets:
ipf -s
To modify packet filtering behaviour:
ipf -Fa (remove both incoming and outgoing rule sets)
ipf -Fo (remove outgoing rules only)
ipf -Fi (remove incoming rules only)
ipf -D (disable all packet filtering)
ipf -E (enable packet filtering)
To view currently loaded rules for the active set:
ipfstat -io
To view currently loaded rules for the inactive set:
ipfstat -I -io
To remove all the runnings rules and load a new set from a file:
ipf -Fa -f filename
To load rules to the inactive rule set:
ifp -I -f filename
To append rules to the current active rule set:
echo "block in log on hme0 proto tcp from any to any port = 25" | ipf -f -
Sample rule set for an Solaris 10 host (192.168.93.128) with one zone (192.168.93.132). The interface name is hme0. We all ssh and icmp echo (ping) only to the host, all else being blocked. All outgoing traffic is allowed and stateful. http is allowed through to the Solaris zone hosted on the server:
pass out quick all keep state
pass in quick on hme0 proto icmp from any to any icmp-type 8 keep state
pass in quick on hme0 proto tcp from any to 192.168.93.128 port = ssh keep state
pass in quick on hme0 proto udp from any to 192.168.93.132/32 port = 80 keep state
block in log all
PaTcH_MsG 8 Version of is not installed on this system
I had to manually run some of the patches in the Solaris patch cluster recently but got this error:
> ./checkinstall: .: filename argument required
> .: usage: . filename
> PaTcH_MsG 8 Version of is not installed on this system.
To fix make sure that the directory tree all the way down to the patch is executable by 'nobody'.
> ./checkinstall: .: filename argument required
> .: usage: . filename
> PaTcH_MsG 8 Version of is not installed on this system.
To fix make sure that the directory tree all the way down to the patch is executable by 'nobody'.
Thursday, March 01, 2007
setuid wrapper
I needed to run a script with root privileges,but had
forgotten that Solaris (and I guess mosts versions of Unix) will not allow setuid on scripts. The solutions is to write a binary wrapper will will call the script:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define myfile "/path/to/script"
main(argc, argv)
char **argv;
{
setuid(0);
seteuid(0);
execv(myfile, argv);
}
forgotten that Solaris (and I guess mosts versions of Unix) will not allow setuid on scripts. The solutions is to write a binary wrapper will will call the script:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define myfile "/path/to/script"
main(argc, argv)
char **argv;
{
setuid(0);
seteuid(0);
execv(myfile, argv);
}
Wednesday, January 17, 2007
Fix for acroread
Adobe reader fails to start on the Gnome desktop on Fedora 6. There
seems to be a conflict withscim (smart common input method).
The fix is to add the following to the top of /usr/bin/acroread:
export GTK_IM_MODULE=ximseems to be a conflict withscim (smart common input method).
The fix is to add the following to the top of /usr/bin/acroread:
Monday, December 04, 2006
GRUB errors
After a migration of my home server to a new mirrored 500GB sata setup from my old 160GB pata system, I encountered some problems with booting the server. Intially booting stopped at:
GRUB _
This was fixed by booting from the FC6 DVD and selecting "linux rescue". I then chrooted to my install with "chroot /mnt/sysimage", followed by a "grub-install".
This fixed my first problem but now boot was hanging at:
GRUB loading stage 2
So again, back into the rescue boot and my chroot environment. Now I ran "/sbin/grub" which took me into the grub shell. I ran "root (hd0,0)" to use the first partition of the boot disk, then ran "setup (hd0).
Next boot all was well.
GRUB _
This was fixed by booting from the FC6 DVD and selecting "linux rescue". I then chrooted to my install with "chroot /mnt/sysimage", followed by a "grub-install".
This fixed my first problem but now boot was hanging at:
GRUB loading stage 2
So again, back into the rescue boot and my chroot environment. Now I ran "/sbin/grub" which took me into the grub shell. I ran "root (hd0,0)" to use the first partition of the boot disk, then ran "setup (hd0).
Next boot all was well.
Friday, December 01, 2006
X Forwarding problems
I've set up a new Fedora 6 server using Xen (another story), but no xorg packages were installed. When logging in over ssh with X forwarding enabled (ssh -X) I still couldn't run any GUI applications remotely. Logging in with debug (ssh -Xv):
debug1: Requesting X11 forwarding with authentication spoofing.
debug1: Remote: No xauth program; cannot forward with spoofing.
Turns out the solution is to install xauth:
# yum install xorg-x11-xauth.i386
debug1: Requesting X11 forwarding with authentication spoofing.
debug1: Remote: No xauth program; cannot forward with spoofing.
Turns out the solution is to install xauth:
# yum install xorg-x11-xauth.i386
Friday, September 08, 2006
Configuring apache for webdav
I wanted to configure my apache server with a webdav directory to test iCal's calender publishing ability. My apache server runs on Fedora Core 5. In /etc/httpd/conf.d I created a file called webdav.conf which along with all the other .conf files in this directory gets read by the master conf file /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf. The file webdav.conf has the following content:
<Location /cal>
DAV On
AuthType Basic
AuthName "WebDAV Restricted"
AuthUserFile /var/www/.htusers
require user myuser
</Location>
The location directive refers to a directory called "cal" located at the root of my webserver created with:
mkdir -p /var/www/html/cal
chown apache:apache /var/www/html/cal
"DAV On" enables the webdav access for this location. I'm using basic apache username/password authentication for a pre-existing user "myuser" in the file /var/www/.htusers.
<Location /cal>
DAV On
AuthType Basic
AuthName "WebDAV Restricted"
AuthUserFile /var/www/.htusers
require user myuser
</Location>
The location directive refers to a directory called "cal" located at the root of my webserver created with:
mkdir -p /var/www/html/cal
chown apache:apache /var/www/html/cal
"DAV On" enables the webdav access for this location. I'm using basic apache username/password authentication for a pre-existing user "myuser" in the file /var/www/.htusers.
Monday, August 28, 2006
Secure IMAP with Dovecot and SSL
In common with many other older protocols IMAP traffic is sent in clear text, with potential for anyone to eavesdrop or steal passwords. Like other modern IMAP servers Dovecot provides methods of enhancing security; you can either use secure authentication methods such as cram-md5 or encrypt the whole session using SSL. I've configured my Fedora Core 5 server to use SSL.
By default on FC5 Dovecot allows the following protocols:
imap imaps pop3 pop3s
To only allow imaps we must set:
protocols = imaps
in /etc/dovecot.conf
The server also comes with a dummy "localhost.localdomain" x509 certificate in /etc/pki/dovecot which should be replaced by at your own self-certified certificate (or even better one signed by a CA). There is a script provided ( /usr/share/doc/dovecot-1.0/examples/mkcert.sh ) to automate the process, but first a two files must be modified. Since mkcert.sh has not been written specifically for FC5 we must change the locations in the script so that they look like:
#!/bin/sh
# Generates a self-signed certificate.
# Edit dovecot-openssl.cnf before running this.
OPENSSL=${OPENSSL-openssl}
#SSLDIR=${SSLDIR-/etc/ssl}
SSLDIR=${SSLDIR-/etc/pki/dovecot}
OPENSSLCONFIG=${OPENSSLCONFIG-/etc/pki/dovecot/dovecot-openssl.cnf}
CERTFILE=$SSLDIR/certs/dovecot.pem
KEYFILE=$SSLDIR/private/dovecot.pem
Of course, these values should match what is in /etc/dovecot.conf, but the above is good for a default install. Next, update the contents of /etc/pki/dovecot/dovecot-openssl.cnf to reflect the local country code, organisation and common name (something other than localhost.localdomain!). Now all that is reuired is to run "mkcert.sh" then run a "service dovecot restart", following which any mail clients will need to be configured for SSL.
By default on FC5 Dovecot allows the following protocols:
imap imaps pop3 pop3s
To only allow imaps we must set:
protocols = imaps
in /etc/dovecot.conf
The server also comes with a dummy "localhost.localdomain" x509 certificate in /etc/pki/dovecot which should be replaced by at your own self-certified certificate (or even better one signed by a CA). There is a script provided ( /usr/share/doc/dovecot-1.0/examples/mkcert.sh ) to automate the process, but first a two files must be modified. Since mkcert.sh has not been written specifically for FC5 we must change the locations in the script so that they look like:
#!/bin/sh
# Generates a self-signed certificate.
# Edit dovecot-openssl.cnf before running this.
OPENSSL=${OPENSSL-openssl}
#SSLDIR=${SSLDIR-/etc/ssl}
SSLDIR=${SSLDIR-/etc/pki/dovecot}
OPENSSLCONFIG=${OPENSSLCONFIG-/etc/pki/dovecot/dovecot-openssl.cnf}
CERTFILE=$SSLDIR/certs/dovecot.pem
KEYFILE=$SSLDIR/private/dovecot.pem
Of course, these values should match what is in /etc/dovecot.conf, but the above is good for a default install. Next, update the contents of /etc/pki/dovecot/dovecot-openssl.cnf to reflect the local country code, organisation and common name (something other than localhost.localdomain!). Now all that is reuired is to run "mkcert.sh" then run a "service dovecot restart", following which any mail clients will need to be configured for SSL.
Friday, August 11, 2006
CUPS Browsing
The CUPS print software ships with the browse support (or rather the broadcast component of the server) disabled. Once enabled, all clients should be able to detect and browse all printers on the server. There are basically three possible configurations (in /etc/cups/cupsd.conf) for broadcast:
BrowseAddress aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd
BrowseAddress @LOCAL
BrowseAddress @IF(name)
The first will specify a broadcast address such as 192.168.0.255. The second will broadcast to all local nets, whilst ignoring LANS such as point-to-point (dial-up) etc. The last limits broadcasts to an interface, so "BrowseAddress @IF(eth0)" only broadcasts on device eth0.
By default the server will allow incoming packets from any address, so if you wish to restrict access you can use either of the "BrowseAllow" or "BrowseDeny" directives as in:
BrowseDeny badhost.example.net (requires "HostNameLookups On")
BrowseDeny 192.168.1.10
BrowseDeny @IF(eth1)
BrowseAddress aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd
BrowseAddress @LOCAL
BrowseAddress @IF(name)
The first will specify a broadcast address such as 192.168.0.255. The second will broadcast to all local nets, whilst ignoring LANS such as point-to-point (dial-up) etc. The last limits broadcasts to an interface, so "BrowseAddress @IF(eth0)" only broadcasts on device eth0.
By default the server will allow incoming packets from any address, so if you wish to restrict access you can use either of the "BrowseAllow" or "BrowseDeny" directives as in:
BrowseDeny badhost.example.net (requires "HostNameLookups On")
BrowseDeny 192.168.1.10
BrowseDeny @IF(eth1)
Friday, August 04, 2006
Solaris and man page troubles
After a fresh install of Solaris I was unable to use "man -k" as I was getting:
/usr/share/man/windex: No such file or directory
The solution is to run "catman -w" and all is well.
/usr/share/man/windex: No such file or directory
The solution is to run "catman -w" and all is well.
Wednesday, July 05, 2006
Xgl on Fedora Core 5
I've got Xgl running by following the instructions here. I've been waiting quite a while for somebody to provide an easy and non destructive way of installing Xgl. I have previously tried using Aiglx, but that didn't seem as stable; blurry fonts and X server hangs when switching between virtual consoles.
Xgl works very well on my desktop (P4 2.8, 1 GB Ram, nVidia fx5700 256MB) with the nVidia driver, but not so well on my laptop (P4 2.4, 1 GB Ram, ATI 340M IGP). As ATI haven't released a linux driver for the 320/340 IGP series I have to use the open source 'radeon' driver which doesn't yet support the pixel-buffer required by Xgl. As a result some of the effects are rendered in software, and some graphical glitches are visible.
To view/modify the shortcut keys for compiz (which provides all the cool effects) you'll need to run 'gconf-editor' and look at 'apps/compiz'.
Xgl works very well on my desktop (P4 2.8, 1 GB Ram, nVidia fx5700 256MB) with the nVidia driver, but not so well on my laptop (P4 2.4, 1 GB Ram, ATI 340M IGP). As ATI haven't released a linux driver for the 320/340 IGP series I have to use the open source 'radeon' driver which doesn't yet support the pixel-buffer required by Xgl. As a result some of the effects are rendered in software, and some graphical glitches are visible.
To view/modify the shortcut keys for compiz (which provides all the cool effects) you'll need to run 'gconf-editor' and look at 'apps/compiz'.
Wednesday, June 28, 2006
Remote name daemon control (rndc) for BIND
Using the rndc command you can send commands to your DNS servers over TCP authenticated by digital signatures. Without any parameters the command prints out its options:
Usage: rndc [-c config] [-s server] [-p port]
[-k key-file ] [-y key] [-V] command
command is one of the following:
reload Reload configuration file and zones.
reload zone [class [view]]
Reload a single zone.
refresh zone [class [view]]
Schedule immediate maintenance for a zone.
retransfer zone [class [view]]
Retransfer a single zone without checking serial number.
freeze zone [class [view]]
Suspend updates to a dynamic zone.
thaw zone [class [view]]
Enable updates to a frozen dynamic zone and reload it.
reconfig Reload configuration file and new zones only.
stats Write server statistics to the statistics file.
querylog Toggle query logging.
dumpdb [-all|-cache|-zones] [view ...]
Dump cache(s) to the dump file (named_dump.db).
stop Save pending updates to master files and stop the server.
stop -p Save pending updates to master files and stop the server
reporting process id.
halt Stop the server without saving pending updates.
halt -p Stop the server without saving pending updates reporting
process id.
trace Increment debugging level by one.
trace level Change the debugging level.
notrace Set debugging level to 0.
flush Flushes all of the server's caches.
flush [view] Flushes the server's cache for a view.
flushname name [view]
Flush the given name from the server's cache(s)
status Display status of the server.
recursing Dump the queries that are currently recursing (named.recursing)
*restart Restart the server.
* == not yet implemented
Version: 9.3.2
Because digital signatures are used for authentication with the name server daemon, you must speicify either a key-file ( -k option) or key on the command line ( -y option). If no key or key-file is sepcified then rndc will look in the rndc.conf file.
So now you can do cool stuff like turn query logging on and off with:
# rndc querylog
# ping -c 1 www.google.com
# tail /var/log/messages
Jun 28 23:48:21 poseidon named[1986]: query logging is now on
Jun 28 23:48:48 poseidon named[1986]: client 192.168.116.10#33362: query: www.google.com IN A +
# rndc querylog
# tail /var/log/messages
Jun 28 23:51:32 poseidon named[1986]: query logging is now off
You can dump the name server cache with the command:
# rndc dumpdb -cache
The dump file will be specified in the named.conf file in the options directive:
dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db";
Since my server runs in a chrooted environment the location is actually /var/named/chroot/var/damed/data/cache_dump.db. The file itself is just plain text so you can view it in any editor.
Usage: rndc [-c config] [-s server] [-p port]
[-k key-file ] [-y key] [-V] command
command is one of the following:
reload Reload configuration file and zones.
reload zone [class [view]]
Reload a single zone.
refresh zone [class [view]]
Schedule immediate maintenance for a zone.
retransfer zone [class [view]]
Retransfer a single zone without checking serial number.
freeze zone [class [view]]
Suspend updates to a dynamic zone.
thaw zone [class [view]]
Enable updates to a frozen dynamic zone and reload it.
reconfig Reload configuration file and new zones only.
stats Write server statistics to the statistics file.
querylog Toggle query logging.
dumpdb [-all|-cache|-zones] [view ...]
Dump cache(s) to the dump file (named_dump.db).
stop Save pending updates to master files and stop the server.
stop -p Save pending updates to master files and stop the server
reporting process id.
halt Stop the server without saving pending updates.
halt -p Stop the server without saving pending updates reporting
process id.
trace Increment debugging level by one.
trace level Change the debugging level.
notrace Set debugging level to 0.
flush Flushes all of the server's caches.
flush [view] Flushes the server's cache for a view.
flushname name [view]
Flush the given name from the server's cache(s)
status Display status of the server.
recursing Dump the queries that are currently recursing (named.recursing)
*restart Restart the server.
* == not yet implemented
Version: 9.3.2
Because digital signatures are used for authentication with the name server daemon, you must speicify either a key-file ( -k option) or key on the command line ( -y option). If no key or key-file is sepcified then rndc will look in the rndc.conf file.
So now you can do cool stuff like turn query logging on and off with:
# rndc querylog
# ping -c 1 www.google.com
# tail /var/log/messages
Jun 28 23:48:21 poseidon named[1986]: query logging is now on
Jun 28 23:48:48 poseidon named[1986]: client 192.168.116.10#33362: query: www.google.com IN A +
# rndc querylog
# tail /var/log/messages
Jun 28 23:51:32 poseidon named[1986]: query logging is now off
You can dump the name server cache with the command:
# rndc dumpdb -cache
The dump file will be specified in the named.conf file in the options directive:
dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db";
Since my server runs in a chrooted environment the location is actually /var/named/chroot/var/damed/data/cache_dump.db. The file itself is just plain text so you can view it in any editor.
Tuesday, June 27, 2006
DB2 upgrade
I had a DB2 V8.1 fixpack 2 installation on one of my FC5 systems which I upgraded to the (currently) latest fixpack 12. After completing the upgrade and running the post install tasks (iupdate) I found I couldn't run any of the utils such as db2cc:
[db2inst1@medusa ~]$ db2cc
stackpointer=0x1c3aa4
Writing Java core file ....
Written Java core to /tmp/javacore11599.1151439455.txt
DB2JAVIT : RC = 11
Oops! Something was clearly very wrong here. It turns out that the Java SDK (1.31) originally installed with DB2 doesn't work with FC5 or my kernel (2.6.17). My problem was resolved by downloading and installing the Java 1.42 SDK rpm from IBM, and running the following command as user db2inst1:
db2 update dbm cfg using JDK_PATH /opt/IBMJava2-142
[db2inst1@medusa ~]$ db2cc
stackpointer=0x1c3aa4
Writing Java core file ....
Written Java core to /tmp/javacore11599.1151439455.txt
DB2JAVIT : RC = 11
Oops! Something was clearly very wrong here. It turns out that the Java SDK (1.31) originally installed with DB2 doesn't work with FC5 or my kernel (2.6.17). My problem was resolved by downloading and installing the Java 1.42 SDK rpm from IBM, and running the following command as user db2inst1:
db2 update dbm cfg using JDK_PATH /opt/IBMJava2-142
Saturday, June 24, 2006
Mirroring websites with wget
I'm sure it's already quite well known, but I've just discovered how to mirror web sites with wget. I'd been wanting to make sure I had a back up of this blog and was already sure that wget would be the tool to use. A quick search turned up this command:
wget --mirror –w 2 –p --html-extension –-convert-links –P /home/pat/documents/blogger/ http://patgardner.blogspot.com
--mirror
get files recursively, but depending on timestamp
-w
wait a number of seconds between retrieval
-p
download all page requisites such as images
--html-extension
makes sure that all the copies of files have .html file extensions
--convert-links
convert links suitable for local viewing
-P
path to save files to
wget --mirror –w 2 –p --html-extension –-convert-links –P /home/pat/documents/blogger/ http://patgardner.blogspot.com
--mirror
get files recursively, but depending on timestamp
-w
wait a number of seconds between retrieval
-p
download all page requisites such as images
--html-extension
makes sure that all the copies of files have .html file extensions
--convert-links
convert links suitable for local viewing
-P
path to save files to
Tuesday, June 20, 2006
iFolder
I've just discovered iFolder, a storage solution originally created by Novell but now released as an open source project. With iFolders you can set up directories to replicate to a server, which in turn will replicate to any other computer that has the client software installed. Client software is available for Windows XP, Linux and OS X. Without the client software you can still upload/download files via the web interface.
Friday, June 16, 2006
Slow Firefox
Firefox 1.5.0.3 provided with Fedora 5 seems very slow (more so on my laptop) particularly when scrolling. Cpu usage can easily hit 100% when scrolling up and down a page. A short term solution until they fix it is to put:
export MOZ_DISABLE_PANGO=1
In your .bash_profile.
export MOZ_DISABLE_PANGO=1
In your .bash_profile.
Zeroconf service discovery
Another new addition to the latest release of Fedora is avahi support, better known as zeroconf or bonjour in the Apple world. This allows for service discovery on the network, such as printers automatically anouncing their presence or bookmarks being broadcast to the LAN. The avahi-daemon takes care of advertising services whilst application such as Gnome (2.14) are avahi aware. Here is an example of how to get avahi up and running.
1. Configure some services. The directory /etc/avahi/services is initially empty, so we'll create a few files:
apache.service
ssh-ftp.service
ssh.service
We populate the files with the following data:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone='no'?>
<!DOCTYPE service-group SYSTEM "avahi-service.dtd">
<service-group>
<name>Apache Server Documentation</name>
<service>
<type>_http._tcp</type>
<port>80</port>
<txt-record>path=/manual</txt-record>
</service>
</service-group>
<?xml version="1.0" standalone='no'?>
<!DOCTYPE service-group SYSTEM "avahi-service.dtd">
<service-group>
<name replace-wildcards="yes">SFTP File Transfer on %h</name>
<service>
<type>_sftp-ssh._tcp</type>
<port>22</port>
</service>
</service-group>
<?xml version="1.0" standalone='no'?>
<!DOCTYPE service-group SYSTEM "avahi-service.dtd">
<service-group>
<name replace-wildcards="yes">Remote Terminal on %h</name>
<service>
<type>_ssh._tcp</type>
<port>22</port>
</service>
</service-group>
2. Enable the avahi-daemon, and have it auto start on system boot.
# service avahi-daemon start
# chkconfig avahi-daemon on
3. We can also enable Gnome file sharing from "Desktop/Preferences/Personal File Sharing" which provides WebDAV access to ~/Public.
4. If we now start nautilus and click on "network" or go to the "network:///" Gnome-VFS, you can see that in addition to the Windows SMB network we also have the "Public" WebDAV share as well as the secure FTP resources displayed:
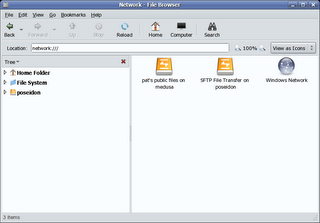
5. Epiphany (the Gnome web browser) is the only browser which supports avahi bookmarks at this time. We can see this working if we start Epiphany:
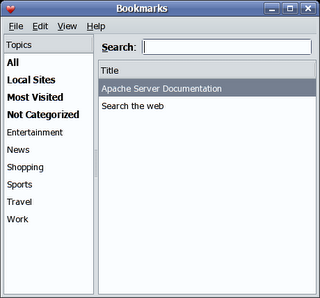
There are a couple of other tools which can display zeroconf services, the avahi provided 'avahi-discover' and the 'Zeroconf discovery applet' which is avaible from the avahi website. Download the service-discovery-applet tarball, unpack and run:
# ./configure && make && make install
You should now be able to add the applet to your gnome-panel:
It's clearly early days for zeroconf support in Linux, but what there is works well. I hope that the Gnome team and other application developers continue to integrate and extend avahi support.
1. Configure some services. The directory /etc/avahi/services is initially empty, so we'll create a few files:
apache.service
ssh-ftp.service
ssh.service
We populate the files with the following data:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone='no'?>
<!DOCTYPE service-group SYSTEM "avahi-service.dtd">
<service-group>
<name>Apache Server Documentation</name>
<service>
<type>_http._tcp</type>
<port>80</port>
<txt-record>path=/manual</txt-record>
</service>
</service-group>
<?xml version="1.0" standalone='no'?>
<!DOCTYPE service-group SYSTEM "avahi-service.dtd">
<service-group>
<name replace-wildcards="yes">SFTP File Transfer on %h</name>
<service>
<type>_sftp-ssh._tcp</type>
<port>22</port>
</service>
</service-group>
<?xml version="1.0" standalone='no'?>
<!DOCTYPE service-group SYSTEM "avahi-service.dtd">
<service-group>
<name replace-wildcards="yes">Remote Terminal on %h</name>
<service>
<type>_ssh._tcp</type>
<port>22</port>
</service>
</service-group>
2. Enable the avahi-daemon, and have it auto start on system boot.
# service avahi-daemon start
# chkconfig avahi-daemon on
3. We can also enable Gnome file sharing from "Desktop/Preferences/Personal File Sharing" which provides WebDAV access to ~/Public.
4. If we now start nautilus and click on "network" or go to the "network:///" Gnome-VFS, you can see that in addition to the Windows SMB network we also have the "Public" WebDAV share as well as the secure FTP resources displayed:

5. Epiphany (the Gnome web browser) is the only browser which supports avahi bookmarks at this time. We can see this working if we start Epiphany:

There are a couple of other tools which can display zeroconf services, the avahi provided 'avahi-discover' and the 'Zeroconf discovery applet' which is avaible from the avahi website. Download the service-discovery-applet tarball, unpack and run:
# ./configure && make && make install
You should now be able to add the applet to your gnome-panel:

It's clearly early days for zeroconf support in Linux, but what there is works well. I hope that the Gnome team and other application developers continue to integrate and extend avahi support.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
